HOUSTON, TEXAS (Isaac Silvestre, Energy Analytics Institute, 24.June.2025, Words: 285) — About one-fifth or 20% of liquefied natural gas (LNG) traded globally in 2024 transited the Strait of Hormuz and primarily from Qatar, according to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA).
And, Asian countries from China, India, Taiwan, and South Korea to Pakistan were the primary end destinations for the bulk of the LNG that transited the strait.
Some of key points about the strait, provided by the EIA in a 24 Jun. 2025 brief, include the following:
— the strait is a critical route for oil and petroleum products as well;
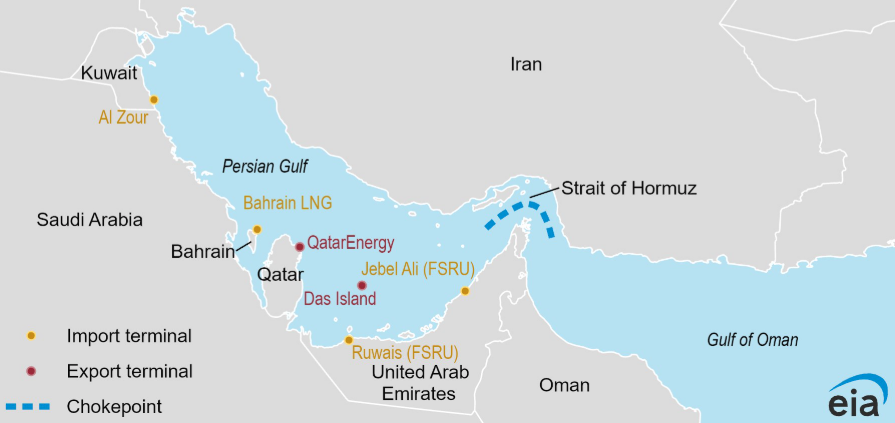
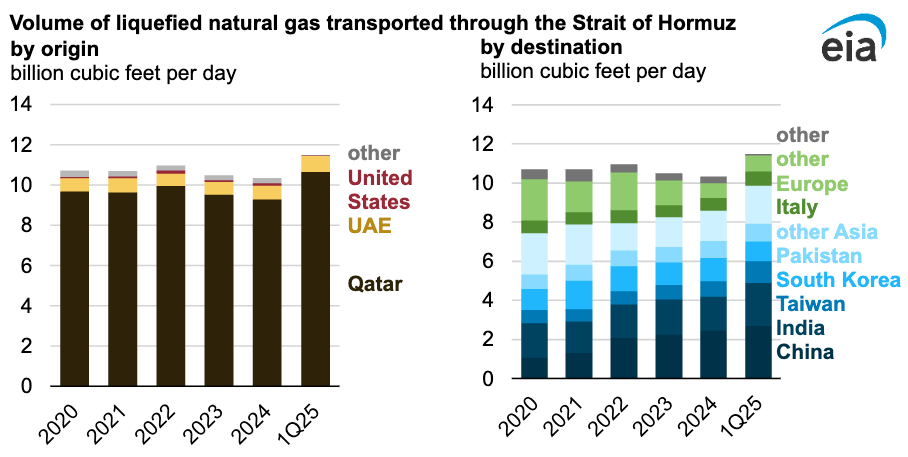
— in 2024, Qatar exported about 9.3 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) of LNG through the strait, while the United Arab Emirates (UAE) exported about 0.7 Bcf/d, accounting for nearly all LNG flows from the Persian Gulf through Hormuz;
— in 2024, an estimated 83% of LNG that moved through the strait from Persian Gulf countries to Asian markets. Importantly, China, India, and South Korea were the top destinations, accounting for 52% of all Hormuz LNG flows in 2024;
— in 2024, disruptions to LNG flows through the Bab al-Mandeb Strait, which connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea, and more US LNG exports to Europe pushed LNG exports from Qatar away from Europe to Asia; and
— Kuwait and the UAE imported LNG that originated outside of the Persian Gulf, including from the US and West Africa. Bahrain began operating an LNG import terminal in Apr. 2025 and also received cargoes that transited Hormuz from outside of the Persian Gulf, including recent cargoes in Apr. and Jun. that originated from the US.
____________________
By Isaac Silvestre reporting from Houston. © 2025 Energy Analytics Institute (EAI). All Rights Reserved.